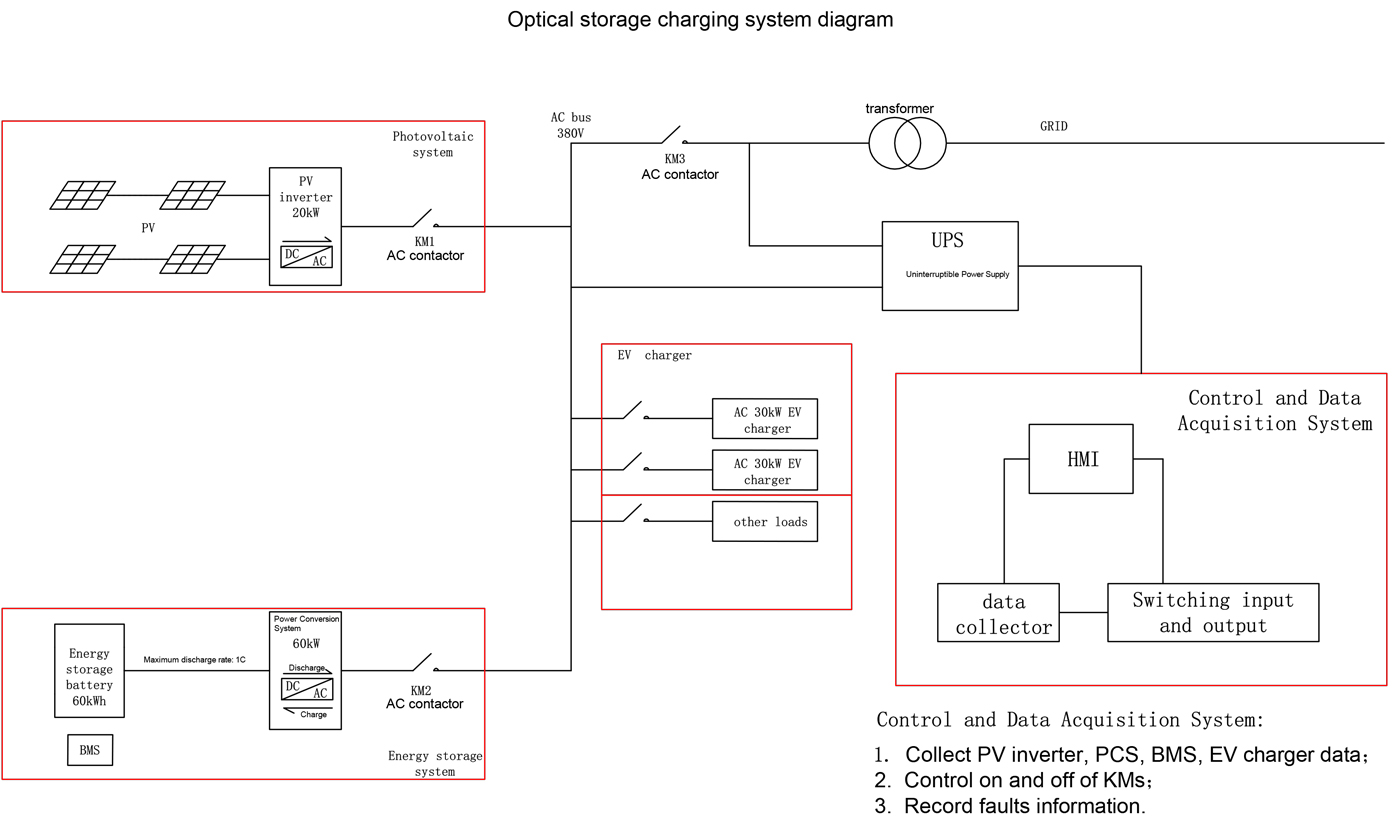
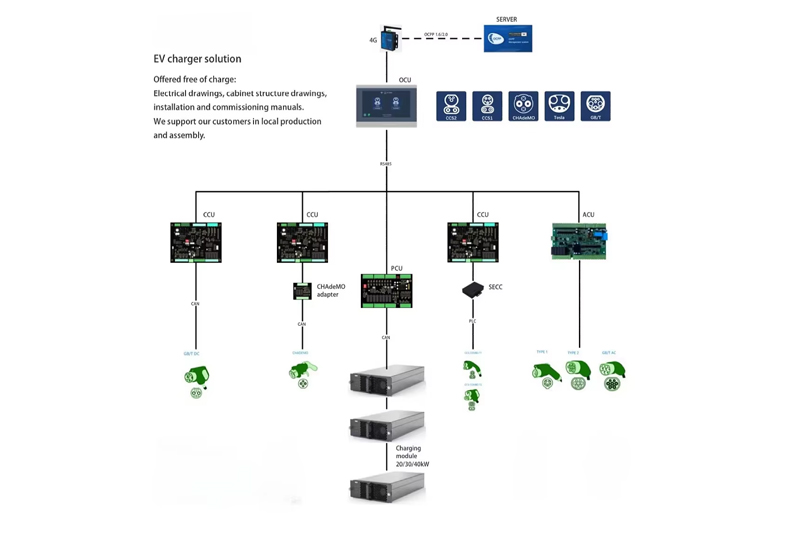
What is bidirectional charging of evs? Bidirectional ev charging vs traditional ev charging
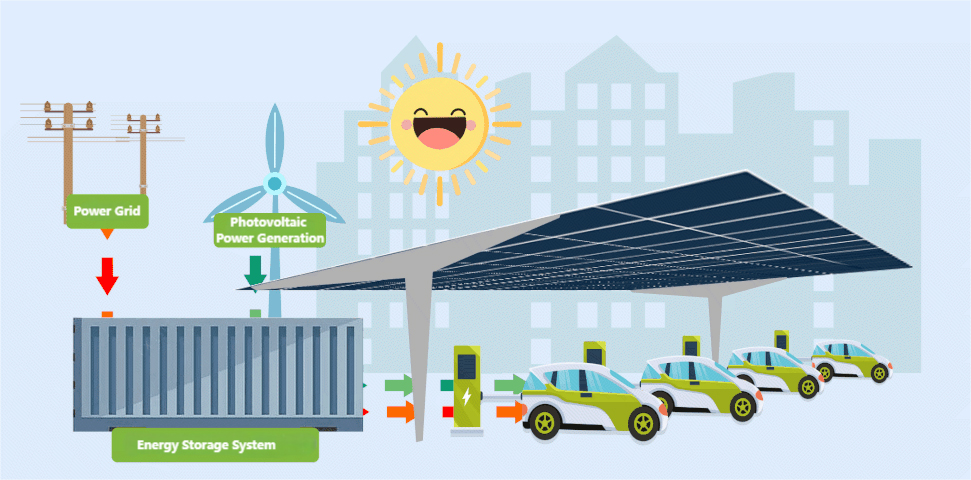
A bidirectional charging system is an innovative technology that enables electric vehicles (EVs) not only to draw power from the grid to charge their batteries but also to send stored electricity back to the grid. This two - way power flow is made possible through specialized charging equipment and vehicle - to - grid (V2G) technology. When an EV is connected to a bidirectional charger, it can function as a mobile energy storage unit, providing electricity to the grid during peak demand periods or storing energy when it is more abundant and cheaper.
Bidirectional charging mode for EVs means the vehicle's ability to switch between charging from the grid and discharging power back to it based on various factors. These factors include grid demand, electricity prices, and the vehicle owner's energy usage patterns. For example, during the day when solar power generation is high and electricity prices are low, the EV can charge its battery. Then, in the evening when households consume more power and electricity prices spike, the EV can supply power back to the grid, potentially reducing the overall electricity costs for the owner and helping to balance the grid load.
In bidirectional charging mode, the vehicle's charging system can communicate with the grid operator through smart grid technology. It receives signals regarding grid conditions such as current demand levels, voltage stability, and real - time electricity prices. Based on this information, the EV can automatically decide whether to charge, discharge, or maintain its current state of charge. This intelligent interaction between the vehicle and the grid not only benefits the individual EV owner but also contributes to the overall stability and efficiency of the electrical grid.
Vehicle - to - home (V2H) charging is an application closely related to bidirectional charging. In a V2H setup, an EV can power a home during power outages or periods of high electricity costs.
Through a transfer switch and appropriate software, the EV can supply electricity to the home's electrical system, running essential appliances such as lights, refrigerators, and heating or cooling systems. This provides an added layer of energy security for households and can also serve as a backup power source in case of emergencies.
Bidirectional EV Charging Vs Traditional Unidirectional EV Charging
Bidirectional EV charging and traditional unidirectional EV charging have distinct differences in how they manage power flow for electric vehicles. Here's a side - side comparison:
Bidirectional EV Charging:
Allows power to flow both from the grid to the vehicle (charging) and from the vehicle back to the grid (discharging).
Enables the vehicle to act as an energy storage resource for the grid, helping to balance load during peak and off - peak hours.
Offers potential financial benefits to the EV owner through selling electricity back to the grid during high - price periods.
Requires more complex charging infrastructure and vehicle - to - grid communication technology.
Traditional Unidirectional EV Charging:
Only allows power to flow in one direction, from the grid to the vehicle for charging purposes.
The vehicle is solely a power consumer, and there is no option to contribute power back to the grid.
Relies on simpler charging equipment and does not require sophisticated grid - vehicle communication for power flow management.
Focuses mainly on replenishing the vehicle's battery for transportation needs.