Electric vehicle charging solutions
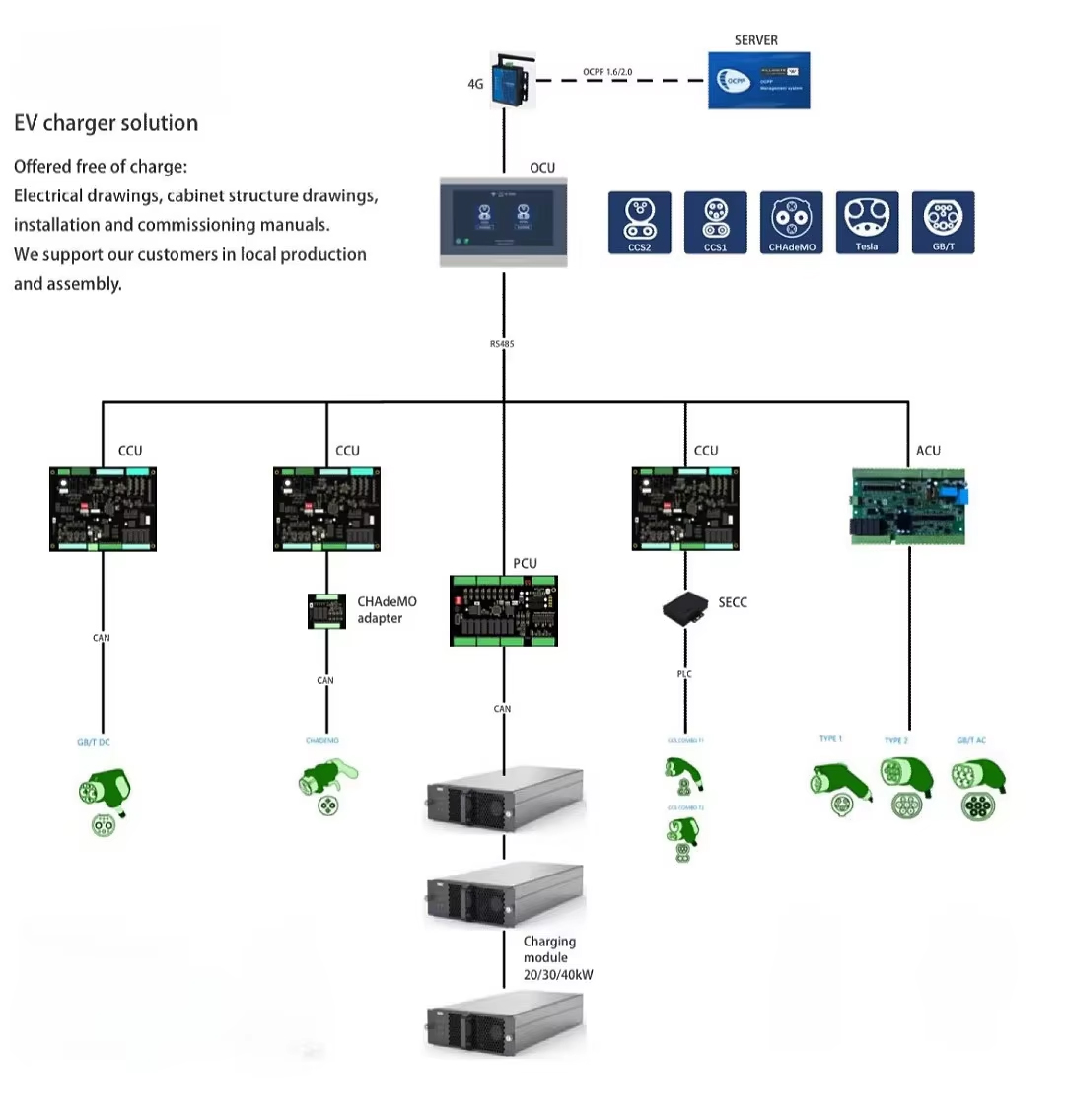
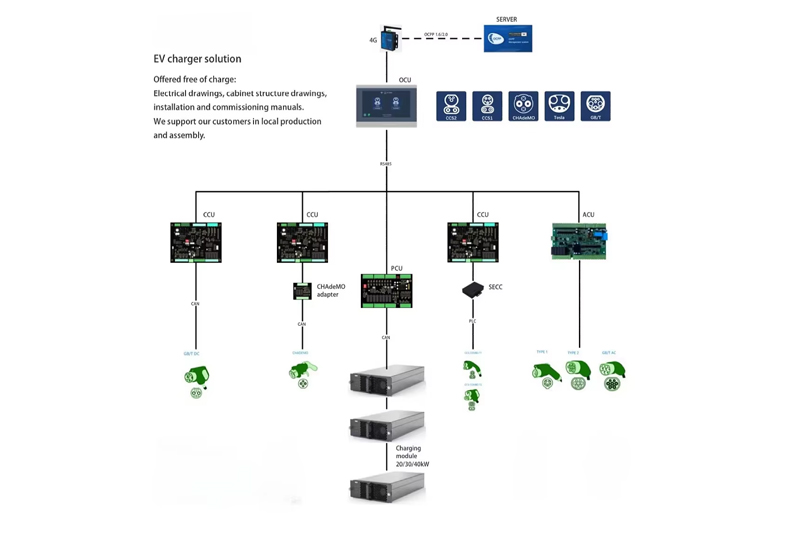
In recent years, the electric vehicle (EV) market has witnessed remarkable growth, driving the demand for advanced and reliable charging solutions. The EV charger solution depicted in the diagram is a comprehensive system designed to meet diverse charging needs, offering both technical sophistication and practical support for customers. This solution stands out by providing free electrical drawings, cabinet structure drawings, as well as installation and commissioning manuals, while also supporting local production and assembly. Such support not only facilitates cost - effective implementation but also ensures quicker deployment and adaptation to local requirements.
At the top of the system, a server is connected via 4G, utilizing the OCPP 1.6 protocol for seamless communication. This connection ensures that the entire charging network can be monitored and managed remotely, enhancing operational efficiency. Below the server is the OCU (Operation Control Unit), a central hub that coordinates the system’s activities. The OCU acts as a bridge, communicating with various components through RS485 and other interfaces, ensuring smooth data flow and control.
The system features multiple CCUs (Charging Control Units), which are pivotal in managing the charging process for different EV standards. These units are compatible with a range of international standards, including CCS2, CHAdeMO, Tesla, and GB/T, making the solution highly versatile. For instance, when an EV equipped with a CHAdeMO connector is plugged in, the CCU, with the help of a CHAdeMO adapter, ensures proper communication and power transfer. The CAN (Controller Area Network) interface used by CCUs allows for reliable and real - time communication with other components, ensuring precise control over the charging process.
In addition to CCUs, there is the ACU (Alternating Current Unit), which handles alternating current charging. This unit is equipped to manage different types of AC charging connectors, catering to the varied needs of EV users. The PCU (Power Control Unit) plays another critical role. It interfaces with charging modules of 20kW, 30kW, or 40kW, optimizing power distribution and ensuring efficient charging. By coordinating with these modules, the PCU can adjust power output based on the EV’s requirements, preventing over - charging and ensuring battery safety.
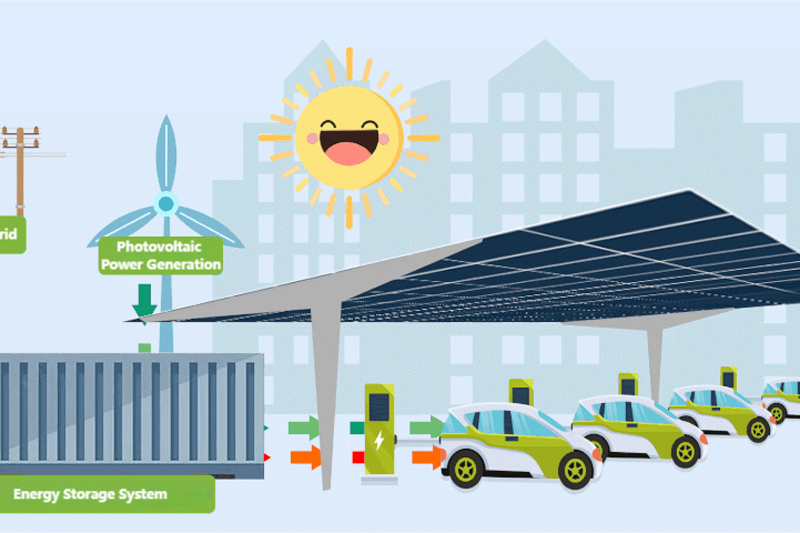
Another notable component is the SECC (Smart Energy Charging Controller), which likely enhances the system’s ability to manage energy flow intelligently. This could involve integrating with smart grids, optimizing charging during off - peak hours, or managing energy storage systems. The use of Type - C and other interfaces further underscores the system’s flexibility in accommodating different hardware setups.
The solution’s emphasis on local production and assembly is a significant advantage. By providing detailed drawings and manuals, companies can manufacture components locally, reducing shipping costs and lead times. This not only boosts local economies but also allows for quicker customization and maintenance. For example, if a component needs repair or replacement, local teams can quickly produce and install it, minimizing downtime.
In conclusion, this EV charger solution is a well - thought - out system that combines technical excellence with practical support. Its compatibility with multiple charging standards, intelligent power management, and support for local production make it a robust choice for EV charging infrastructure development. As the world transitions towards sustainable transportation, such comprehensive solutions will play a vital role in accelerating EV adoption, ensuring that charging is reliable, efficient, and accessible for all users.