As electric vehicle (EV) adoption surges, the demand for efficient EV car chargers has become critical. According to the International Energy Agency, there are over 1.5 million public charging points globally. This growth highlights the need to select an appropriate EV car charger.
Choosing the right charger isn't straightforward. You need to consider various factors, including charging speed, installation requirements, and compatibility with your vehicle. A Level 2 charger can deliver up to 30 miles of range per hour, making it a popular choice for home installations. However, it may require a dedicated electrical circuit, which complicates the decision.
Many users face challenges navigating the myriad of options. They often overlook guidelines or underestimate their charging needs. It's essential to evaluate your unique situation and future needs, even if the landscape can seem overwhelming. Ultimately, the right EV car charger can enhance your driving experience and ensure your vehicle stays charged and ready.

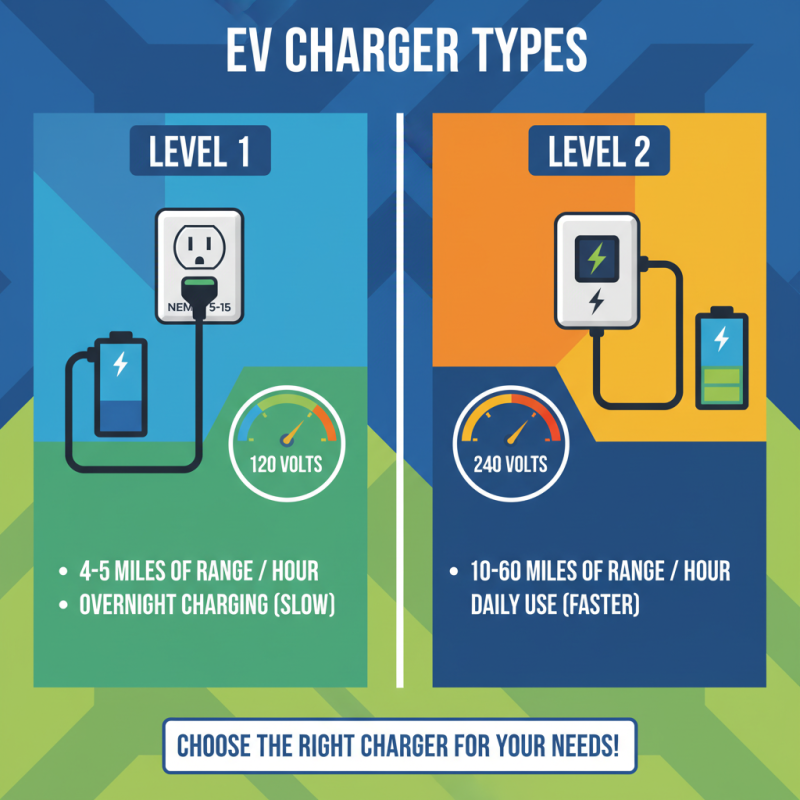
When exploring EV chargers, it's crucial to understand the different types available. Level 1 and Level 2 chargers are the most common in residential settings. A Level 1 charger uses a standard 120-volt outlet and typically delivers about 4-5 miles of range per hour of charging. It’s convenient but slow, making it suitable for overnight charging. In contrast, Level 2 chargers operate on 240 volts, providing 10-60 miles of range per hour. They are more efficient for daily use, especially for those who drive long distances.
DC fast chargers represent the fastest option. They can recharge an EV to 80% in about 30 minutes, depending on the vehicle and charger. A report by the International Energy Agency (IEA) states that as of 2022, global charging infrastructure is vital for enhancing EV adoption. However, many consumers face a tricky dilemma: higher charging speeds often come with higher installation costs and require specific electrical setups.
As more options emerge, it's essential to consider your driving habits and electrical capabilities. Data suggests that nearly 80% of EV owners charge at home, yet the lack of public charging stations can cause anxiety for some users. Factors like cost, installation complexity, and charging speed should be evaluated carefully. This evolving market means there’s no one-size-fits-all solution, forcing buyers to think critically about their choices.
When considering an EV charger, understanding your home's electrical system is crucial. Traditional homes often have 100-amp or 200-amp panels. A 240-volt Level 2 charger typically requires at least a 100-amp service. According to the U.S. Department of Energy, many homes fall below this standard, making compatibility a concern.
Evaluating your wiring is another important step. Older homes might have outdated wiring that cannot support the additional load of an EV charger. This can lead to tripped breakers or worse, fire hazards. It's essential to check the gauge and type of wire used in your home. A report from the Electric Power Research Institute highlights that around 30% of homes might need some upgrades before installation.
Consider your charging needs as well. If you plan to charge overnight, ensure the charger is compatible with your electrical panel's schedule. Some panels may not handle a simultaneous load from an EV charger and other appliances. Assess local electrical codes too. Regulations can vary, leading to additional modifications. Always think about these aspects before choosing the right charger for your home.
| Charger Type | Charging Speed (miles per hour) | Voltage | Amps | Best for |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Level 1 Charger | 4-5 mph | 120V | 12-16A | Home Charging (overnight) |
| Level 2 Charger | 15-30 mph | 240V | 20-40A | Faster Home Charging |
| DC Fast Charger | 100-200 mph | 480V | 100-400A | Public Fast Charging |
Choosing the right EV car charger can be tricky. Understanding the differences between Level 1 and Level 2 chargers is crucial.
Level 1 chargers use a standard home outlet. They provide around 4-5 miles of range per hour. This option is convenient but slow. Ideal for overnight charging, many find this adequate for daily use.
On the other hand, Level 2 chargers offer faster charging speeds. They can deliver 10-60 miles of range per hour. This is beneficial for those who drive longer distances regularly.
However, they require a dedicated circuit and professional installation. Some may underestimate the importance of proper installation. Without it, the charger could be inefficient or even hazardous.
When deciding, consider your driving habits. Do you often need a quick charge? Or do you have sufficient time to fill up overnight? Be aware that if you choose Level 2, the upfront cost is higher.
But the convenience could outweigh those initial expenses. Think about your home setup and parking availability too. Not every home is suitable for a faster charger.
When selecting an EV charger, key features are vital for meeting your needs. Charging speed is a primary consideration. Level 2 chargers typically provide up to 25 miles of range per hour. In contrast, Level 1 chargers offer roughly 4 to 5 miles per hour. If you have a long daily commute, a faster charger will save you time.
Connectivity is another essential feature. Many advanced EV chargers have smartphone apps for monitoring. According to recent industry reports, over 40% of users prefer chargers with smart features. This connectivity allows for remote start, scheduling, and energy usage tracking. However, ensure the charger is compatible with your vehicle. Compatibility can be confusing, causing frustration during installation.
Installation location is equally important. Consider if you need indoor or outdoor installation. Chargers must endure various weather conditions if set outside. Additionally, think about the amperage. While most residential circuits offer 30 to 50 amps, higher amperage allows for quicker charging. However, this may require upgrades to your home's electrical system. Reflect on future needs as well. As EV technology evolves, think about how your charging requirements might change.
This chart compares different types of EV chargers based on their charging speed, measured in miles of range per hour. When selecting an EV charger, consider the charging speed as one of the key features based on your daily driving needs.
When it comes to EV chargers, costs and installation can vary greatly. Studies show that the average cost of a Level 2 home charger ranges from $600 to $2,000. Installation fees add another $300 to $1,500, depending on your home's electrical setup. It's crucial to assess your current electrical system before making a choice. An older home may need an upgrade, increasing expenses.
Consider where you’ll install the charger. A garage installation may be simpler compared to a driveway setup. The latter might require more extensive wiring. According to a report by the U.S. Department of Energy, approximately 80% of EV charging occurs at home. Thus, investment in a reliable home charger pays off in the long run.
Not every installation process is seamless. Homeowners often encounter unexpected challenges. Uneven surfaces, distance from the power source, or local regulations can complicate things. Research local permits and codes ahead of time. Skipping this step could lead to delays and additional costs. Costs are important, but understanding your unique needs is equally essential.






